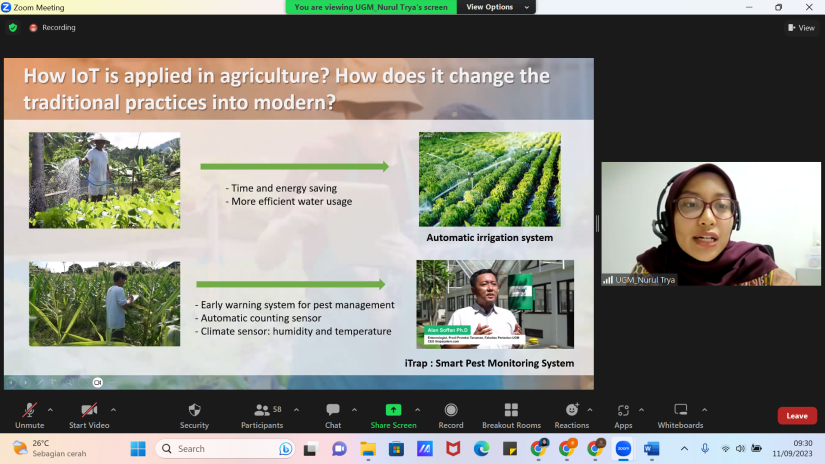
IoT is a connection between more than one device in which data exchange occurs. Examples of IoT applied in the world of agriculture are automatic irrigation systems, I-Trap for monitoring pests, and the use of drones for spraying fertilizers and pesticides. The Agricultural Economics and Agribusiness Study Program, Universitas Gadjah Mada held a guest lecture of the Regional Economics course on September 11th 2023 with speaker Nurul Trya Wulandari, Manager of the Digital Extension Society for Agriculture Application (DesaApps). This guest lecture carried the Development of the Internet of Things theme in the Agribusiness Sector and its role in Regional Development, which was moderated by Muh Amat Nasir, S.P., M.Sc (Lecturer in Regional Economics).
Nurul Trya Wulandari said that Desa Apps is one of the institutions that facilitates forums in implementing IoT. This application functions as a data collection platform. This data is important to support agriculture in terms of:
- Data: Name of land owner/cultivator, land coordination point, type of commodity, harvest time, land area, number of harvests, planting time, and planting system
- Information: Land ownership status, land location, harvested/not harvested, productivity/yield potential, age of rice plants, and planting system used
- Knowledge: Know the names of farmers who meet the criteria to receive compensation assistance from AUTP with a value proportional to their land area
- Wisdom: Coordination between village officials, farmer groups or farmer group associations, and PPL for distribution of compensation to farmers
Challenges in the era of agricultural digitalization include 1) some manual work/done by humans being replaced by automated machines, 2) sectoral ego (unwillingness to share data), 3) data privacy and security, 4) inadequate internet access in some areas, and 5) the presence of imported commodities that are sold at low prices. Solutions that can be taken to face this challenge are increasing digital literacy among farmers, cadre formation of young farmers for modern agricultural rebranding, increasing the quality and quantity of farmers in terms of IT, data integration, improving agricultural infrastructure, and resource efficiency.